
While the kinematic viscosity is given as cSt, m 2/s, and ft 2/s The output dynamic viscosity is given as Pa*s, N*s/m 2, cP, mPa*s, lb f*s/ft 2 and lb m/(ft*h), The calculator below can be used to calculate ethane dynamic or kinematic viscosity at given temperatures and atmospheric pressure. Tabulated values of ethane viscosity and viscosity units conversion are given below the figures. Absolute or dynamic viscosity is used to calculate Reynold's Number to determine if a fluid flow is laminar, transient or turbulent. This also means that it can be used in many dimensionless numbers to compare ratios of diffusivities, and hence the relative importance of different physical processes.The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to gradual deformation by shear stress or tensile stress.įor further definitions, go to Absolute (dynamic) and kinematic viscosity. The transport of momentum is analogous to the transport of other properties of a fluid. The kinematic viscosity can also be called diffusivity of momentum since it has the same dimensions as the diffusivity of heat and diffusivity of mass concentration. It is also expressed in terms of centistokes (cSt or ctsk). The Stokes(St) is the cgs physical unit for kinematic viscosity, named after George Gabriel Stokes, where 1 St = 10 -4 m 2/s.
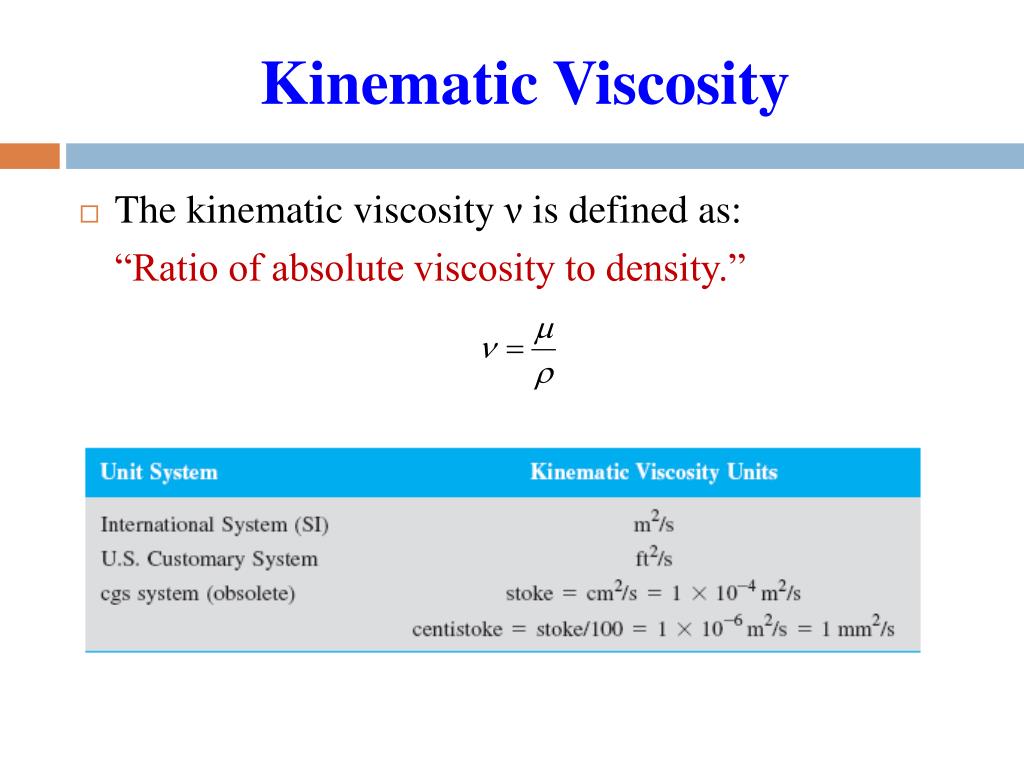
Where ν = kinematic viscosity, μ = absolute or dynamic viscosity, ρ = density.

Kinematic viscosity can be obtained by dividing the dynamic viscosity of a fluid by its density. Kinematic Viscosity is the ratio of absolute or dynamic viscosity to density - a quantity in which the force is external and independent of the mass of the fluid. a fluid with less viscosity will take less time to flow than a fluid with higher viscosity). The higher the viscosity, the longer it takes to flow through the tube (i.e. The liquid is placed in the container and allowed to flow by gravity. Kinematic viscosity can be measured using a device called a capillary viscometer which consists of a graduated canister with a narrow tube at the bottom. For example cream becomes butter if agitated. Such fluids can become solid when flowing within a pipe. Those fluids that increase their viscosity with the increase in agitation or pressure under constant temperature are called Shear Thickening Fluids or Dilatant Fluids. They appear to be thick or viscous but they can be pumped quite easily. Those fluids which reduce their viscosity, when agitation or pressure is increased, keeping temperature constant, are known as Shear Thinning Fluids or Thixotropic Fluids. Most common liquids and gases are Newtonian fluids, such as water, oil and air. Types Of Fluid Newtonian Fluidsįluids in which shearing stress is linearly related to rate of shearing strain are called Newtonian fluids or true liquids, since agitation or pumping at constant temperature does not affect their viscosity or consistency. The kinematic viscosity of a liquid usually decreases with increase in temperature whereas the kinematic viscosity of a gas increases.
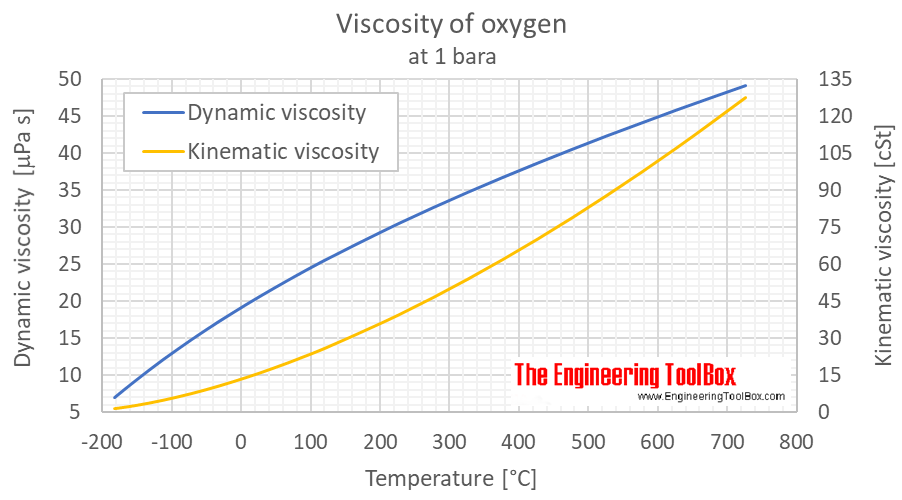
The kinematic viscosity is highly dependent on temperature. Usually a thin liquid like water has less viscosity as compared to a thick fluid like honey having high viscosity. It can be thought of as fluid friction or internal resistance of a fluid to flow, and specifically the kinematic viscosity measures the resistance to flow of a fluid under the influence of gravity (or some other body force acting on the mass of the fluid).

In general it is the "thickness" of a fluid. The resistance of a fluid that is being deformed from shear stress or extensional stress is called viscosity.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
